The Human-Machine Advantage: Why AI Skills are the New Performance Differentiator

Over the next 3 to 5 years, the ability of an employee to partner with artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance human productivity in many jobs. According to Gartner, “37% of organizations have implemented AI in some form, demonstrating not just a growing acceptance of AI technology but also an increasing integration of AI skills within business processes.”
Employees who adopt AI effectively—augmenting their human capabilities by leveraging the human-machine partnership—will, over time, outperform those who cannot. Identifying those who can maximize their productivity by working effectively with AI creates a unique challenge for employers when assessing candidates and employees.
AI-Human Partnership will Impact Productivity in Some Jobs More than Others
As the graphic below illustrates, not all positions require the same degree of AI integration. This blog explores jobs where mastering AI collaboration can unlock major productivity gains. These types of jobs pose the biggest disruption for employers, creating a need for a distinct evaluation framework to gauge performance in occupations that combine human capabilities with machine or technology.
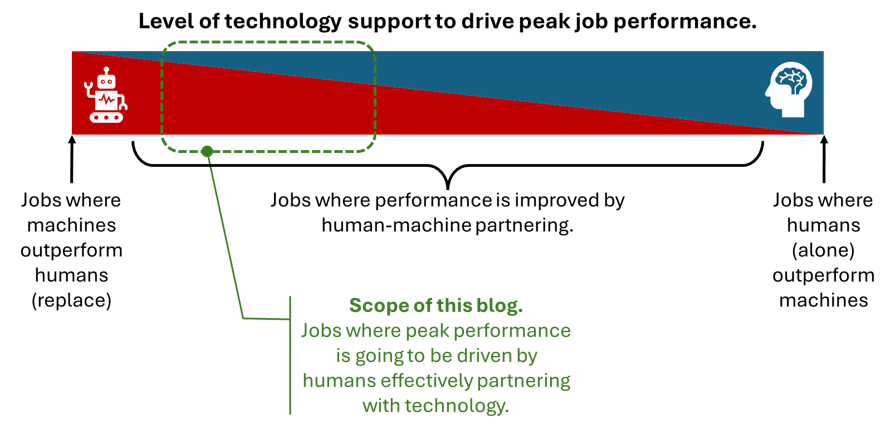
Jobs where effective partnering with technology enhances human performance
Characteristics of Jobs Improved by Human-Machine Partnering
There are a range of jobs with characteristics, such as speed of processing large amounts of data, accurately analyzing information to extract insights, and identifying trends and patterns, where performance will be significantly impacted by the partnership of human capabilities with those of AI. Criteria for occupations where human and AI partnership will improve productivity include jobs requiring:
- Speed and Accuracy
- Anomaly Detection
- Data Processing
- Trend Analysis
- Pattern Recognition
- Predictive Modeling
Occupations Enhanced by AI
Occupations that require a high volume of quantitative and/or qualitative analysis will benefit from the adoption of AI skills. Roles that include highly repetitive tasks including content creation, marketing and advertising, and customer support can also be automated using AI tools to enhance human productivity and performance. The table that follows shows sample occupations and their potential for AI partnership.
| Occupation | Potential AI Partnership |
| Medical Diagnostics and Imaging | Radiologists who use AI-assisted tools can detect subtle anomalies more accurately and quickly in medical imaging |
| Financial Analysis and Trading | Financial analysts can leverage AI algorithms to process market data, identify trends, and makes informed investment decisions faster |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Logistics managers who utilize AI algorithms can optimize routes, reduce transportation costs, and improve delivery efficiency |
| Scientific Research and Drug Discovery | Researchers using AI models can analyze vast datasets, discover patterns, and accelerate drug development |
Beyond Resumes: Assessing the Skills Needed to Thrive with AI
Integrating AI skills into the workforce and identifying candidates who are most likely able to partner with AI to maximize their productivity is a new challenge for recruiting and assessing the workforce of the future. The organization must identify and assess the characteristics of employees with a higher aptitude and likelihood for AI adoption and determine the most effective way to evaluate those individuals.
Employees will need to acquire a range of skills, as simple as prompting a model to generate content, or as complex as deploying an AI-based data security solution to safeguard their data and infrastructure. Key skills like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning are also essential for successful AI integration. Employees will need to digitally upskill not only to maintain a standard of performance but also to continuously evolve as tools and emerging technologies advance.
Companies looking to develop, assess, and sustain a competitive advantage with the AI skills of their workforce will first need to document the core and specialized skills for their employees to be successful. They must then inventory the knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) of their current employees by conducting skills-based assessments designed to look for proficiency with AI.
Using this information, organizations can conduct a gap analysis of the skills of their workforce and identify developmental areas related to AI. Companies can then develop customized hiring and training strategies through upskilling, reskilling, and the acquisition of new talent to maximize productivity by effectively using AI.
Barriers to Effective AI Skills Assessment
Several barriers can hinder an organization’s ability to evaluate the development of AI skills including a lack of data accessibility and quality, insufficient infrastructure and computing resources, inadequate data literacy, ethical and legal considerations, and resistance to change and culture. These barriers can prevent organizations from identifying KSAs that result in greater productivity.
The challenge for employers, as the graphic below shows, becomes how to capably measure the difference in performance across candidates with and without AI capabilities. An effective evaluation process that measures the value of AI skills in current and potential employees is vital to the future success of an organization.
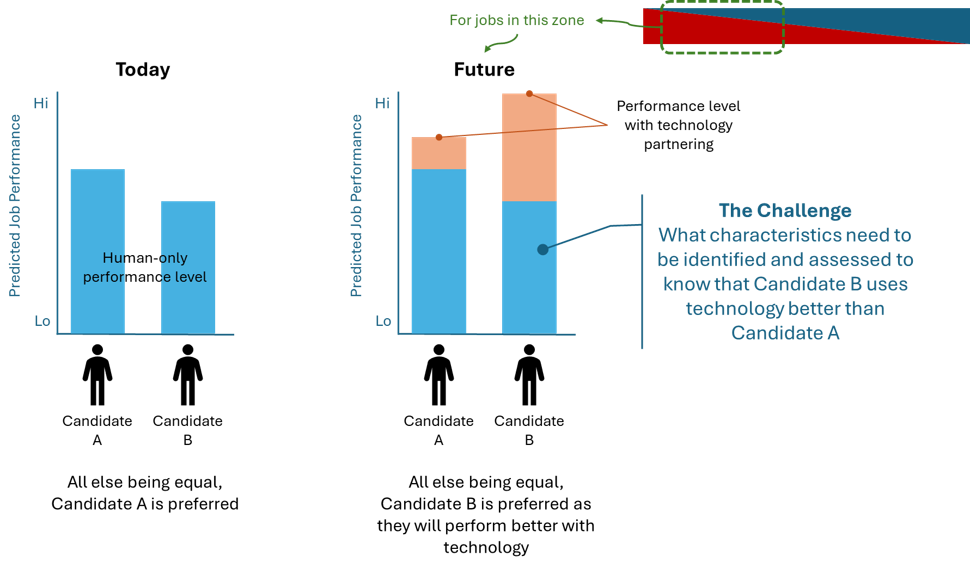
Optimizing the Workforce in the Age of AI: Assessing Skills and Adapting Performance Measures
With a rapidly evolving workforce, organizations need more fluid, flexible methods to measure performance accurately. An organization must determine how AI adoption will impact their hiring process and what steps to take to adapt to evolving needs.
Effectively inventorying a workforce’s skills allows organizations to understand their employees’ strengths and weakness when working with AI. This not only enables the organization to optimally use AI technology but also ensures that tasks are allocated to individuals with the right skillset.
Building a Data-Skilled Workforce Through Assessment and Development
In a recent engagement, Toffler Associates (TA) conducted a workforce forecasting initiative to help a Department of Defense (DoD) client understand the KSAs necessary for future data roles supporting their digital transformation. This work benefited the organization by measuring employee proficiency in data skills and identifying where to invest in data skill development. For example, knowing that statistical analysis is critical for data scientists, hiring managers and supervisors can add pre-employment screenings and skills assessments as an input to hiring decisions.
TA then developed several recommendations for leadership to acquire the talent needed for future data roles including upskilling and reskilling current employees, strategic collaboration with universities, and recruiting from emerging technology hubs. These recommendations were designed to address the specific needs of the DoD client in developing a talent pipeline of data skilled candidates.
This same methodology can be applied to organizations looking to assess and mature their workforce’s proficiency with AI. Understanding the demands of an AI-skills-driven workforce and identifying the supply of qualified candidates are essential to support organizational growth. This analysis can inform the development of a customized hiring and assessment strategy to address gaps in the workforce and keep pace with the growing need for talented AI professionals.
Building the Foundation by Addressing Data Challenges for Skills Development
For the same DoD client, TA developed a comprehensive approach to overcoming barriers to digital skill development. To address data quality, the team is helping foster a culture of data-driven decision-making that encourages employees to leverage data in their work.
Improving digital skills first entails identifying the combination of KSAs different roles require. Data Role Cards detail specific responsibilities and technical skills for different roles, while Personas highlight potential use cases, goals, needs, and pain points. Role-Based Learning Maps provide targeted training recommendations for data professionals to streamline their skill development. These improved definitions of role expectations and identification of skills gaps lay the groundwork for ultimately improving assessment.
As with digital skills, organizations can develop similar learning maps for AI skills to give more concrete guidance on AI upskilling pathways. By conducting a thorough assessment of AI skill needs, identifying skill gaps, and developing targeted recommendations for talent acquisition and development, organizations can create a comprehensive AI upskilling roadmap.
AI Integration & Assessment: Building a Winning Strategy for Talent Acquisition and Performance
Expanding the workforce’s proficiency with AI skills improves decision-making and fosters improved collaboration between human and AI systems. The employees of the future must be able to work with these systems and leverage their capabilities to augment their own processes. A workforce equipped with the knowledge of how to use and interpret AI can reveal untold opportunities for innovation and growth.
To develop a workforce of the future, and maintain a strategic competitive advantage, organizations will need to develop strategies for better and faster AI adoption. They will also need to transition toward assessments that measure the adoption of AI skills for talent acquisition and development.
It is essential that organizations foster an environment that is receptive to the rapidly changing landscape of this transformative technology. Integrating AI skills into the workforce and appropriate assessment methods into a performance management system will increase the success and potential of an organization.
- Categories
- Futures and Foresight
- Workforce of the Future


 About the Authors
About the Authors