Intelligent Automation: Three Questions to Prepare for the Future

This blog post is co-authored with Roboyo, a company delivering intelligent automation solutions for today’s dynamic organizations.
In an era of radically transformative change which is disrupting and redefining traditional business models, a clear understanding of the following topics can make the competitive difference between winning and losing. To both maximize immediate impact and make sure you future proof your investments, we suggest addressing three key questions:
- How will Intelligent Automation disrupt your industry in the next 2-10 years?
- What should you expect of your future employees in an intelligent automation environment?
- What is the future context of customers, competitors, and employees to future proof today’s investments in intelligent automation?
Intelligent automation can be applied in many areas of your business; however, organizations must take a holistic approach to maximize value and understand the forces of change influencing the future.
Intelligent Automation is Reshaping Business
While some organizations may believe they have time before understanding and preparing for Intelligent Automation, this technology already is an integral part of our daily routines. Alexa, a 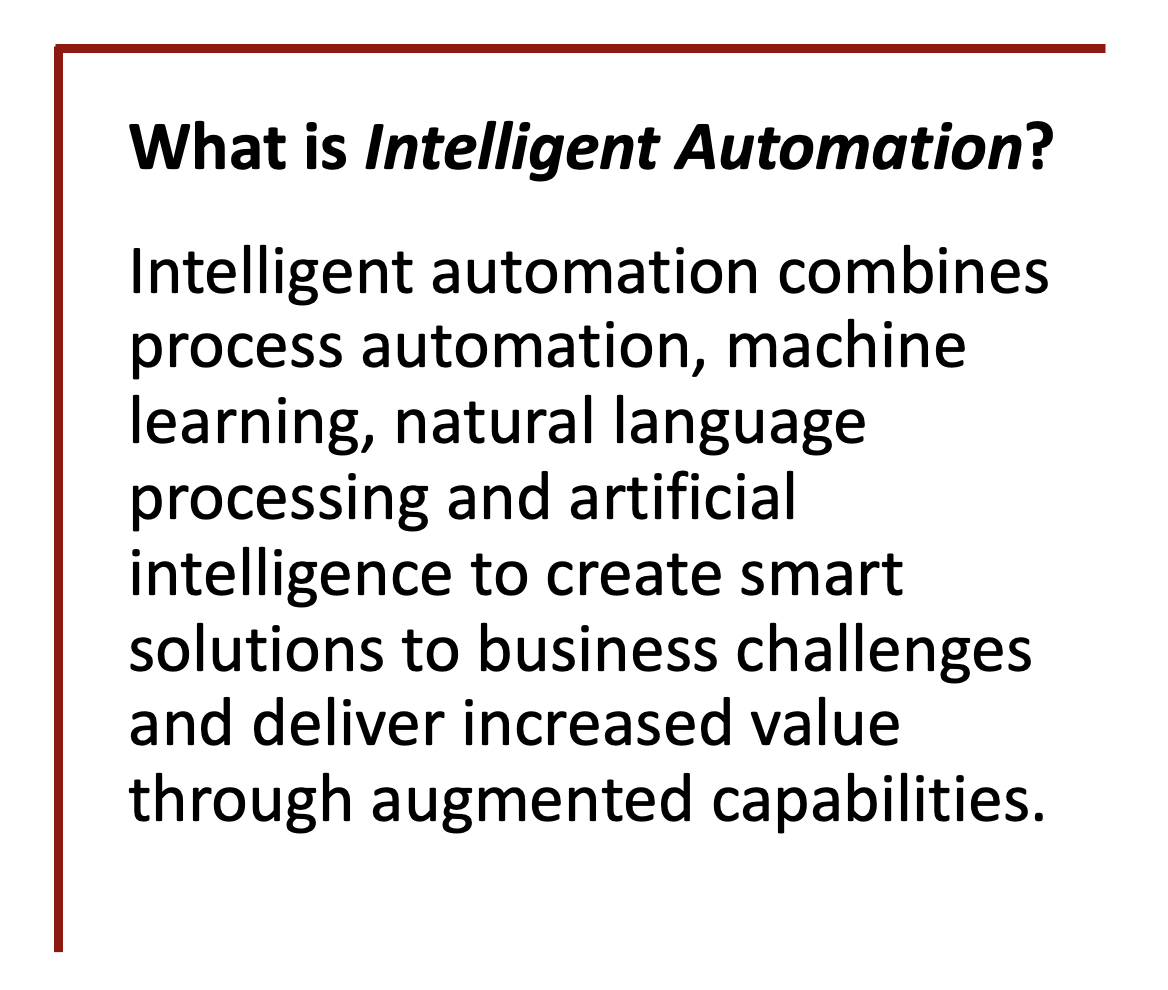 bot (short for “robot”), reads stories to children and plays music with voice cues for seniors; the onset of the pandemic drove interactive sales bots engaging in dialog with prospective customers via email, as well as qualifying sales opportunities; traffic reporting coupled with commuting advice…the list is endless. As in our private sphere, Intelligent Automation also has entered the business sector.
bot (short for “robot”), reads stories to children and plays music with voice cues for seniors; the onset of the pandemic drove interactive sales bots engaging in dialog with prospective customers via email, as well as qualifying sales opportunities; traffic reporting coupled with commuting advice…the list is endless. As in our private sphere, Intelligent Automation also has entered the business sector.
A recent MIT study clarifies, “Improvements in technology adversely affect wages and employment through the displacement effect, in which robots or other automation complete tasks formerly done by workers. Technology also has more positive productivity effects by making tasks easier to complete or creating new jobs and tasks for workers. The researchers said automation technologies always create both displacement and productivity effects, but robots create a stronger displacement effect.” Read the MIT Article.
Trends in Intelligent Automation
During the last five years, perhaps the most apparent manifestation of change in the workforce is the ubiquity of intelligent automation technologies. Automation solutions create and update case management files for insurance companies, execute journal entries for banks and manage invoices to support procurement teams. Executives, managers, and office staff around the globe increasingly face demands to interact or even collaborate with digital workers – computer-generated “bots” that range from desktop macros all the way to multi-application solutions with interactive voice capabilities. As workers and companies around the globe shape the new norms of post-Covid dynamics, business leaders are in a race to build the strategies and operating models necessary to integrate a distributed workforce with software-driven solutions that change how people work. Bank of America analysts refer to these worker-robot collaborations as “robo sapiens,” and others refer to them as collaborative robots, or “cobots.”
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a critical part of Intelligent Automation. It is an innovative technology which automates structured business processes. RPA works just like one of your  employees, interacting with the user interfaces of your existing applications and carrying out structured processes automatically. Automated solutions which use RPA can provide a company with many benefits including, increased productivity, reduced costs, and accelerated ROI.
employees, interacting with the user interfaces of your existing applications and carrying out structured processes automatically. Automated solutions which use RPA can provide a company with many benefits including, increased productivity, reduced costs, and accelerated ROI.
In 2016, RPA began appearing as the buzzword du jour in presentations and sales pitches around the globe. By 2019, the global RPA software market achieved a valuation of $1.41 billion dollars, and predictions for double-digit growth persist through at least 2024. Today, RPA is prevalent throughout many business sectors, including insurance, energy and utilities, manufacturing, healthcare, banking, and financial services. According to a 2019 study commissioned by UiPath, a leading RPA technology vendor, and conducted by Forrester Consulting, 86% of respondents indicated increased efficiency, 57% reported enhanced customer service and 57% reported increased employee engagement.
Software sales growth is only one indicator in a complex network of trends resulting from the rapid and pervasive adoption of RPA, content intelligence applications, machine learning and natural language processing. According to Pitchbook, since 2010 RPA is considered an emerging trend. With the 185 RPA companies they are analyzing, there has been 244 deals and $8.76B capital invested.
RPA + Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of RPA with AI takes software bot capabilities to a whole new level beyond rule-based processing.
These trends span strategy, operations and the technology mix underpinning all aspects of business in the 21st century. Coupled with the Macro Forces of Change that influence our collective futures (described below), the ascendency of automation is shifting the lives of every member of the workforce, personally and professionally.
Impact on the C-Suite Agenda
Senior executives find themselves grappling with changing customer demands, new contests for competitive primacy and an ever-evolving technology landscape. Coupled with the social and economic headwinds engendered by the Covid-19 pandemic, leaders are embracing intelligent automation as a force multiplier when managing cost, efficiency, and business continuity challenges. 67% of executives agree they plan to accelerate the pace of implementation, and 90% anticipate increasing the investment in automation to increase workforce capacity over the next three years.
Successfully transitioning from investment and application implementation to workforce enablement requires a profound shift in methods and communication. Helping managers and employees to understand the motives for adopting automation requires a clear and well-communicated vision aligned with the company’s purpose and values. Automation may be the vehicle, but durable, visceral transformation occurs first and foremost at the human level. The shortest path to success with tools like RPA and chatbots is defined by customers or employees willing to adopt the new tools. Progressing from the c-suite agenda to integrate operations requires leadership to distill the vision into a comprehensible strategy and operating model and engage at every level iteratively and continually.
The Emerging Hybrid Workforce
The composition and distribution of the workforce is shifting not only at a headlong pace but in ways that startle even the analysts. Across many organizations and industries, the demand for higher cognitive, socio-emotional, and technological skills are often at loggerheads with the immediacy of ever-faster productivity demands. The McKinsey Workforce Institute’s 2018 study 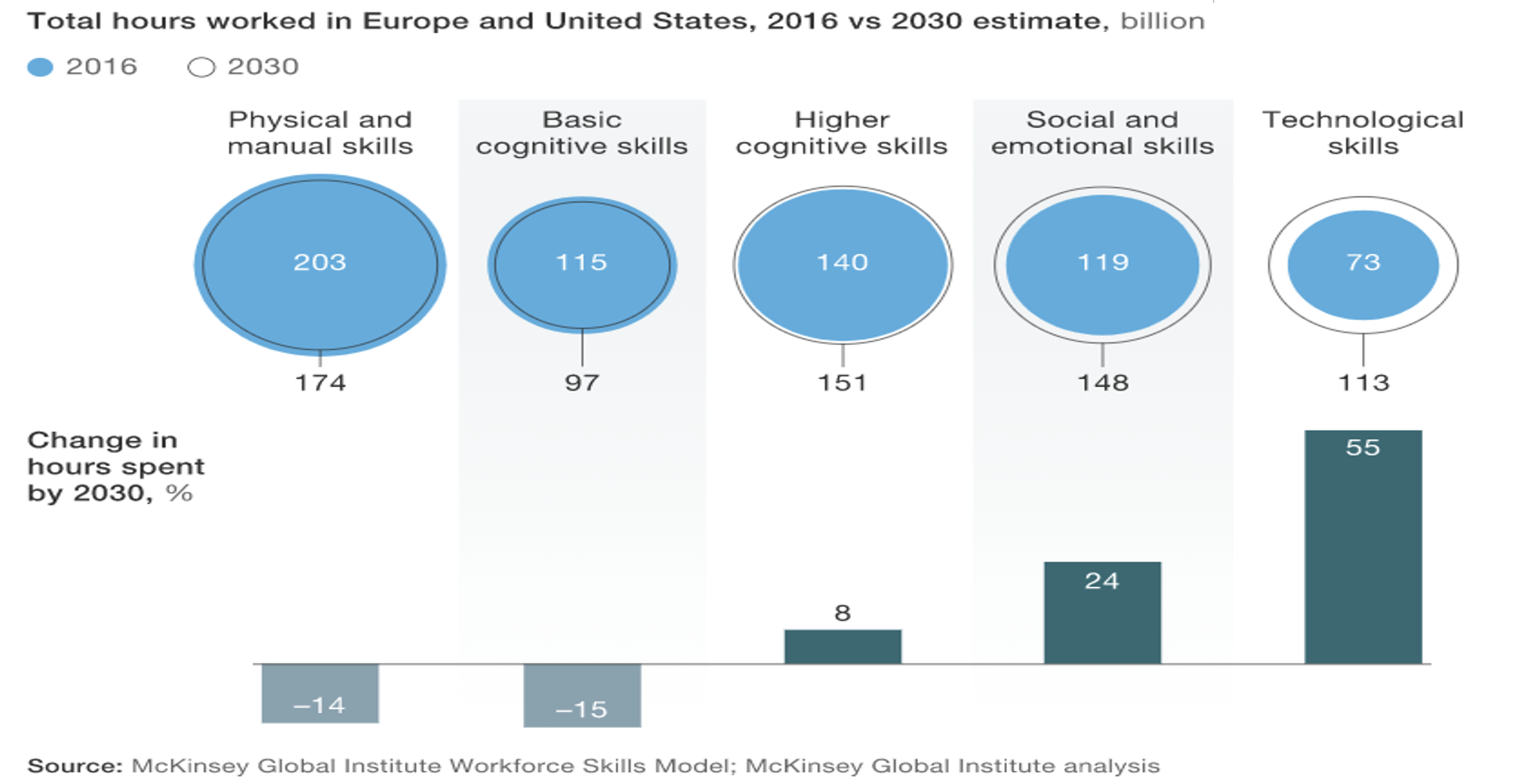 cited the drastic shift in the competencies deemed critical for the evolving workforce. By 2030, the study predicts that employees will spend 41% to 50% more time using technological skills.
cited the drastic shift in the competencies deemed critical for the evolving workforce. By 2030, the study predicts that employees will spend 41% to 50% more time using technological skills.
Leading enterprises are now beginning to ask how they can organize a blended workforce of humans and automation to leverage the complementary strengths each offers. How can they use automation to enable humans to make the most of their abilities, rather than replace them? Does the workforce trust the bots and learn to partner with them?
Without a clear plan, consistent communication and deep engagement, workers throughout the hierarchy can be circumspect. In fact, just 15% of workers believe their organization can manage the change successfully. That stark statistic is indicative of the need for commitment to a people-focused automation strategy. The hybrid organizational chart will inevitably include bots, but not considering and planning for potential displacement, either real or perceived, can have catastrophic implications.
There’s more to this than bold, all-hands notifications trumpeting the need to embrace the future. Effective leaders will begin by first evaluating the continuum of work the company does, assessing where intelligent automation augments the impact of human effort or can provide the capacity to shift people to higher-impact opportunities. Where automation can provide the highest impact with minimal or no human intervention, training and enablement are essential to bridge the gap between uncertainty and adoption.
Understanding the Macro Forces of Change and Developing an Intelligent Automation Roadmap
Before adopting intelligent solutions into an organization, it is essential to develop a roadmap to ensure success – one where employees and managers also have bought into the company’s vision. Many of these technologies can offer immediate and measurable impacts to productivity, quality and even revenue acceleration. However, they are neither a panacea nor the commercial philosopher’s stone, transforming leaden activities into golden profits. Despite all the talk of chatbots, machine learning and robotic processing, intelligent automation needs to be focused on the human experience. Customer and employee experiences are at the core of every successful automation strategy, and as the pace of adoption increases, successful leaders will need to deepen their commitment to understanding and managing the forces driving change in the workforce and how technology can enhance employee’s ability to succeed in an increasingly dynamic present.
When planning to adopt Intelligent Technologies, it is critical for organizations to look beyond the technology disruptions and construct a holistic perspective on these forces which pushes to examine policy, environment, biology, psychology, and societal elements within the ecosystem. When evaluating the forces of change driving the future of automation in the workforce, several Macro Forces of Change should be evaluated in the context of your business:
MACRO FORCES OF CHANGE
| 1. POWERSHIFTS
Shifts in the balance of power across political, economic, and human entities transcend traditional boundaries and frameworks will disrupt how governments and businesses operate. In the last two years, there’s been a 78% increase in job posts on LinkedIn that mention work flexibility5 demonstrating the power of the workforce and causing new HR policies and resource competition. |
5. SECURITY EVERYWHERE Disruptive technology, an increasingly connected society, and novel techniques, create an increasingly complex landscape. This feeling of ubiquitous threats ripples into the personal lives of employees and the data security of the extended organization network into employees’ homes. We are developing a security-everywhere mindset which bridges macro threats with micro security. |
| 2. SOCIETAL COALITIONS AND COLLISIONS Global connectivity creates new relationships while shifting beliefs and expectations create clashes with traditional shared assumptions and social norms. These new tribes influence beliefs around skills and development. The half-life of a skill is currently five years and likely will continue to decrease.3 |
6. TRUST ELASTICITY
Connected humanity creates new relationships among people and institutions with differing behaviors and customs, which strains trust of others; AI/ML enables an arms race between creation and detection of misinformation, which strains trust of content. Individuals who experience epidemics between ages 18 to 25 are 5.1% less likely to have confidence in the national government, and 6.2% less likely to approve the performance of the political leaders.2 |
| 3. BIO-DIGITAL CONVERGENCE
Pervasive and invasive technology further integrates humans and machines impacting human performance, policies, data privacy, and ethics. Research has found that up to 50 percent of time spent on job activities across all sectors could be automated with current technology.4 |
7. RESOURCE SCARCITY
Growing demand for limited resources like energy, water, rare earth minerals, and food, due to global population growth and climate migration, creates conflicts over control of limited resources. Automation and real-time tracking across supply chains increased during pandemic to mitigate risks. |
| 4. INFRASTRUCTURE ADAPTATION
The convergence of physical, cyber and human infrastructure creates a smart, boundaryless, global “interstructure,” which improves efficiency but increases friction between those who do or do not embrace this integration. Supporting a more virtual and global workforce, 95% of the world’s population will have access to the internet in 2030, up from 60% today.1 |
8. DISAGGREGATION OF LOCATION AND ACTIVITY Pandemic physical distancing accelerates the virtualization of life; disconnecting location from activities alters work, learning, commerce, and social norms and geographic movement. Organizations are struggling to determine the best way to bring employees back to the office while keeping in mind the requirements for future like talent acquisition and learning. |
Equally important is the need to understand the key factors that might influence your specific industry, and how to recognize and mitigate risk. While initial investments in intelligent solutions can be focused on point solutions, as intelligent automation grows, this approach will lead to suboptimization and rework. We recommend starting with the end in mind and in the future with an outside-in approach and approach building your automation roadmap at an enterprise level to ensure a comprehensive perspective. As with most disruptive technology, the impact is felt by the humans, employees or customers, interacting with the new technology. As organizations prepare for implementing RPA, they must take a human centric approach to planning the change.
Toffler Associates and Roboyo tackle these concepts and more in an interactive webinar The Future of Work is Now: Strategies for Intelligent Automation and Talent Transformation. Watch to learn more about developing your automation roadmap and the value and risks of RPA for your organization.
1 21 Technology Tipping Points We Will Reach by 2030, businessinsider.com
2 Gallop World Polls, blogs.lse.ac.us
3The Future of Work in Technology, deloitte.com
4 Developing Future Talent, JFF.org,
5 LinkedIn Global Talent Trends 2019, business.linkedin.com
- Categories
- Workforce of the Future


 About the Authors
About the Authors